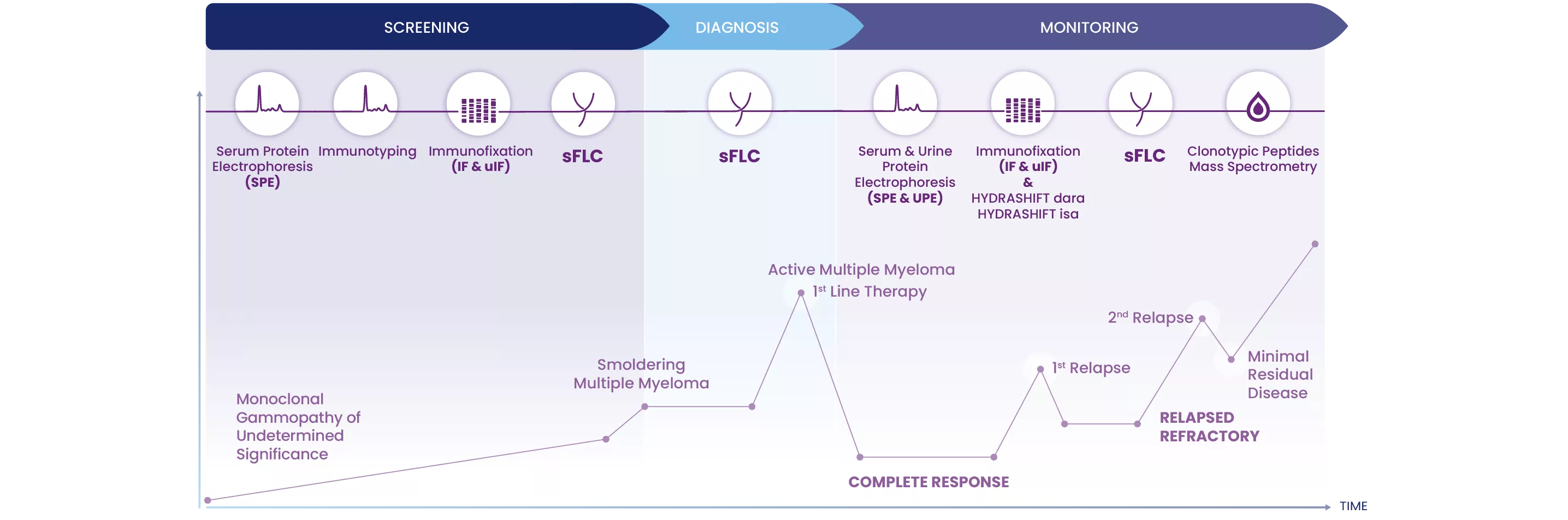
Focus on M-protein Testing

Serum Protein Electrophoresis

Immunofixation

Hydrashift
Sebia Hydrashift removes interfering immunotherapies, like daratumumab and isatuximab, from immunofixation results. This is useful to help accurately interpret immunofixation results when a patient is receiving these therapies since the treatment itself mimics a M-protein.

Free Light Chain
Serum Free Light Chain ratio (sFLC) is a blood test that measures the ratio of free kappa to free lambda light chains of antibodies. An abnormal ratio indicates, but does not confirm, a plasma cell disorder.